Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar, also known as glucose. It occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Without proper management, diabetes can lead to serious complications, making it essential to understand its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Types and Causes of Diabetes
There are different types of diabetes, with the most common being Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes, the most prevalent form, occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough of it. Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth but may increase the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Diabetes
Diabetes symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common signs include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurry vision. Some individuals may also experience slow-healing wounds and recurrent infections. Early detection and proper management are crucial to preventing complications associated with diabetes.
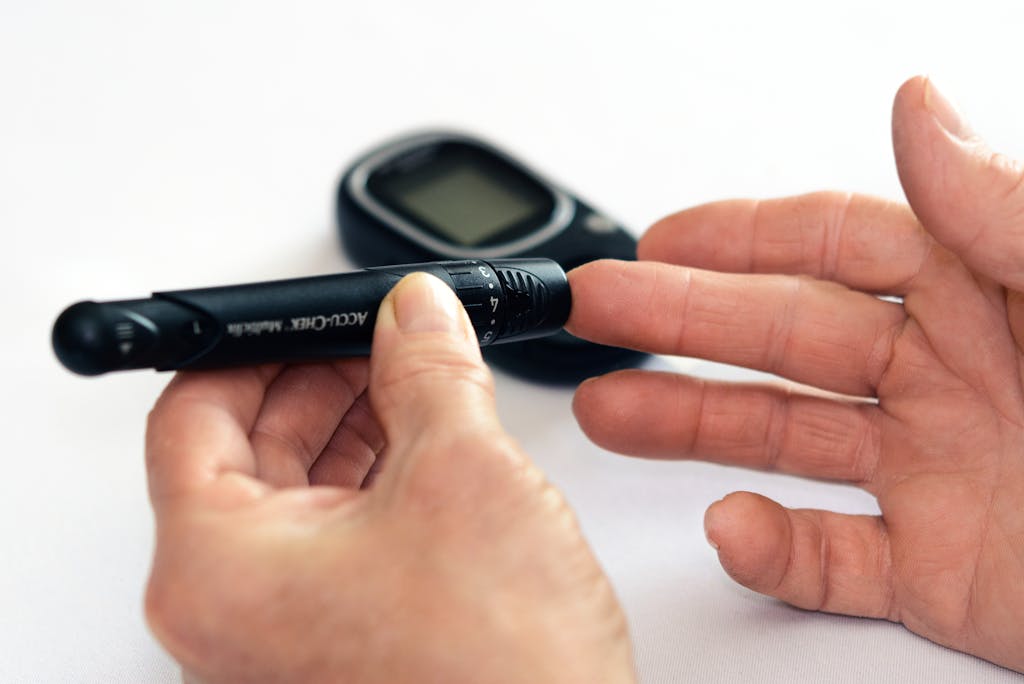
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment
Diagnosing diabetes typically involves blood tests to measure blood sugar levels. The fasting blood sugar test, oral glucose tolerance test, and A1C test are commonly used to confirm the condition. A healthcare provider may also check cholesterol levels and kidney function, as diabetes can impact overall health. Regular monitoring and medical evaluations help in managing the condition effectively.
Treatment and Management of Diabetes
Managing diabetes requires a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. People with Type 1 diabetes rely on insulin therapy, while those with Type 2 diabetes may use oral medications, insulin, or a combination of both. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins, along with regular physical activity, plays a key role in controlling blood sugar levels. Monitoring blood glucose levels and following a prescribed treatment plan are essential for long-term health.
Preventing Complications of Diabetes
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, keeping blood sugar levels within the target range, and attending regular medical check-ups can help prevent these complications. Proper foot care, eye exams, and blood pressure management are also critical in reducing health risks associated with diabetes.
Living Well with Diabetes
With the right approach, individuals with diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. Educating oneself about the condition, making informed dietary choices, staying physically active, and adhering to prescribed treatments contribute to better health outcomes. By taking proactive steps and working closely with healthcare professionals, people with diabetes can effectively manage their condition and enhance their overall well-being.